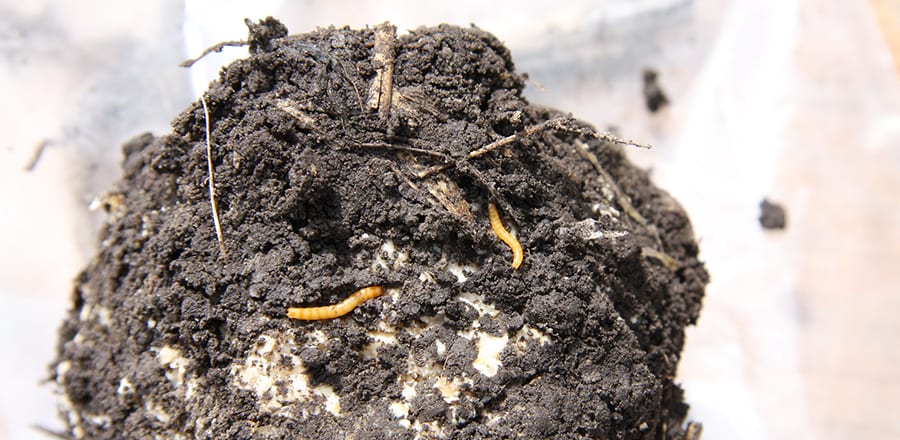
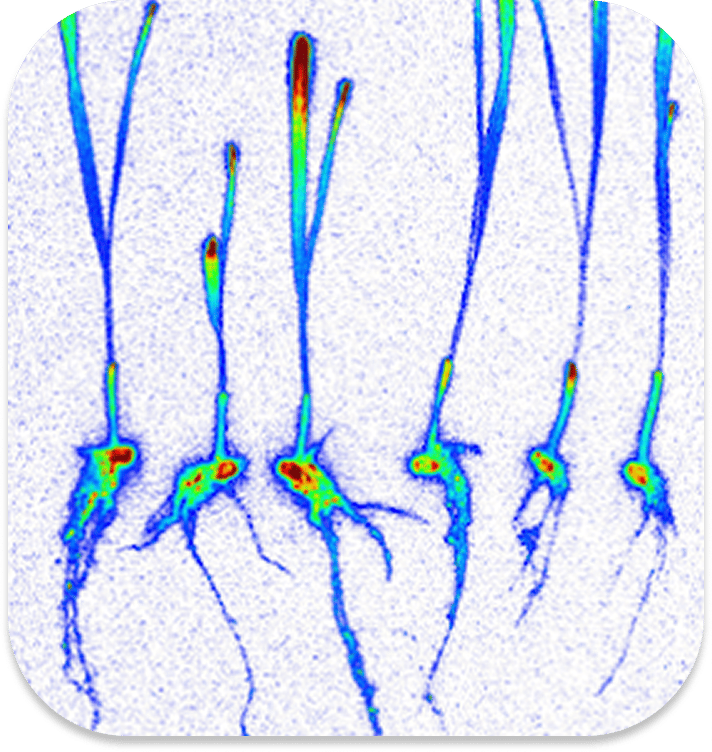
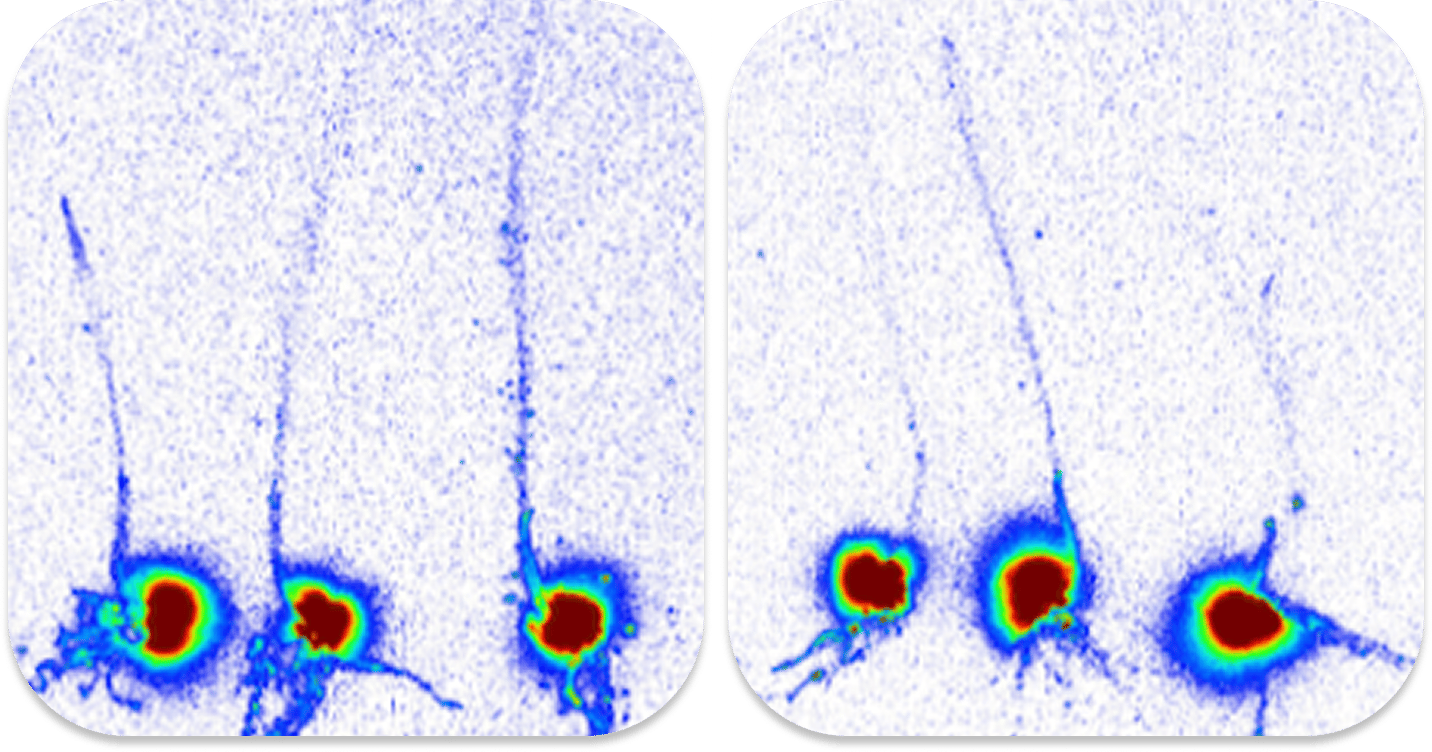
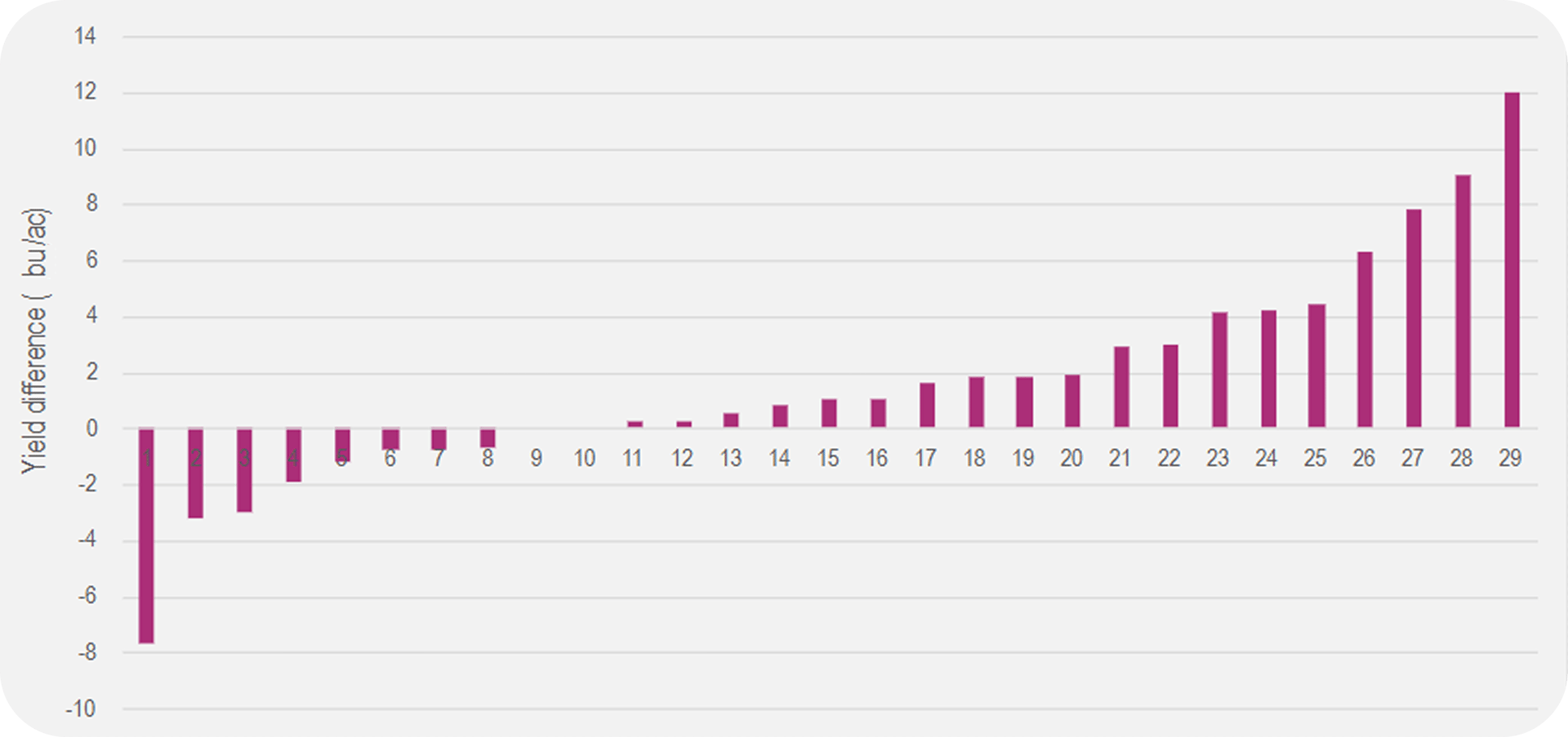Scouting will help you identify the presence and extent of wireworms in your soil. Use bait balls or wheat traps ahead of planting to identify if wireworms are present. In season, leverage Vernon pitfall traps to monitor click beetle (mature wireworms) populations, capture mating males, and reduce egg laying in problem areas. Watch for signs of wireworm feeding, including hollow seeds, dead seedlings, shredded stems, and/or gaps and thinning in otherwise healthy stands.
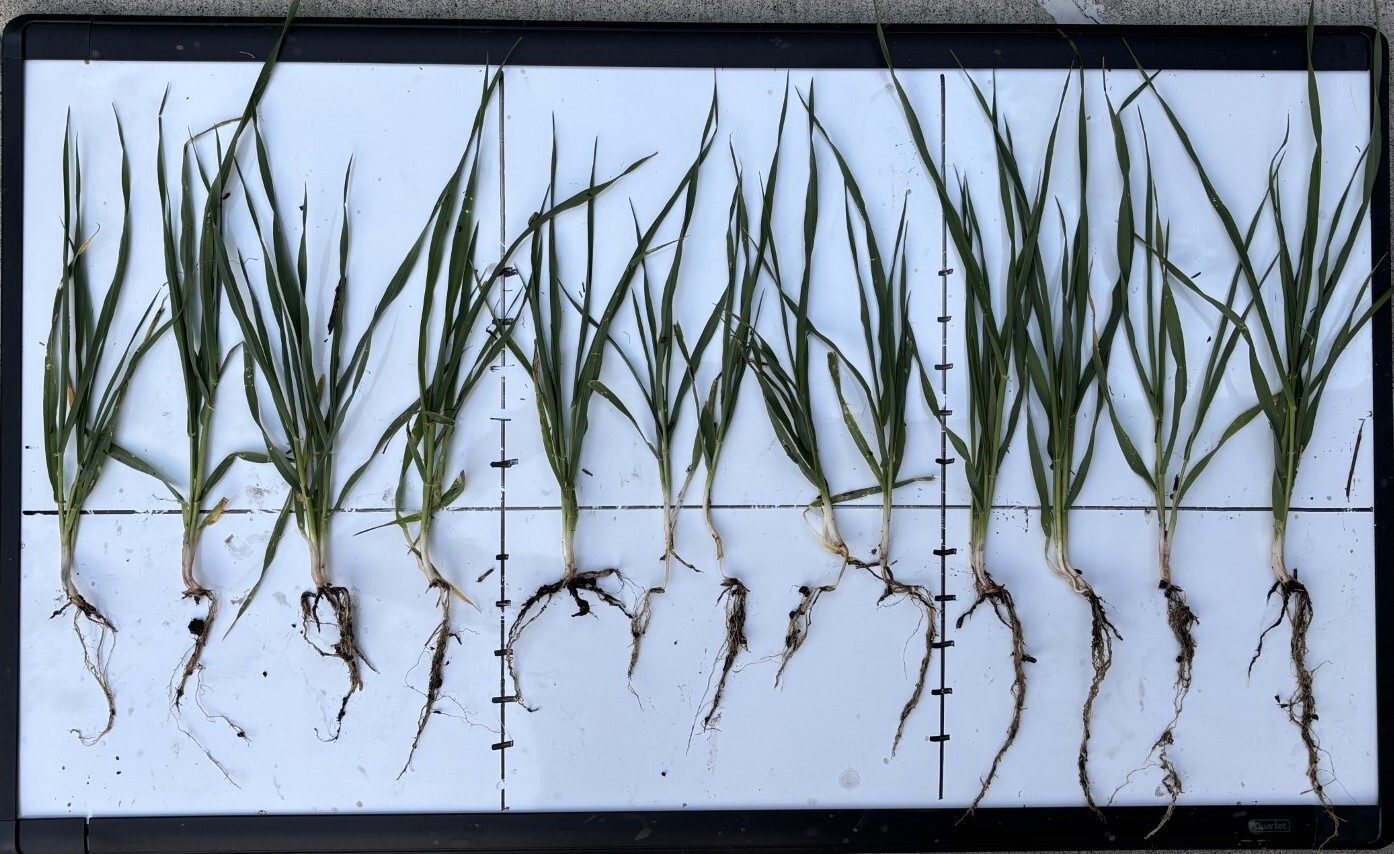
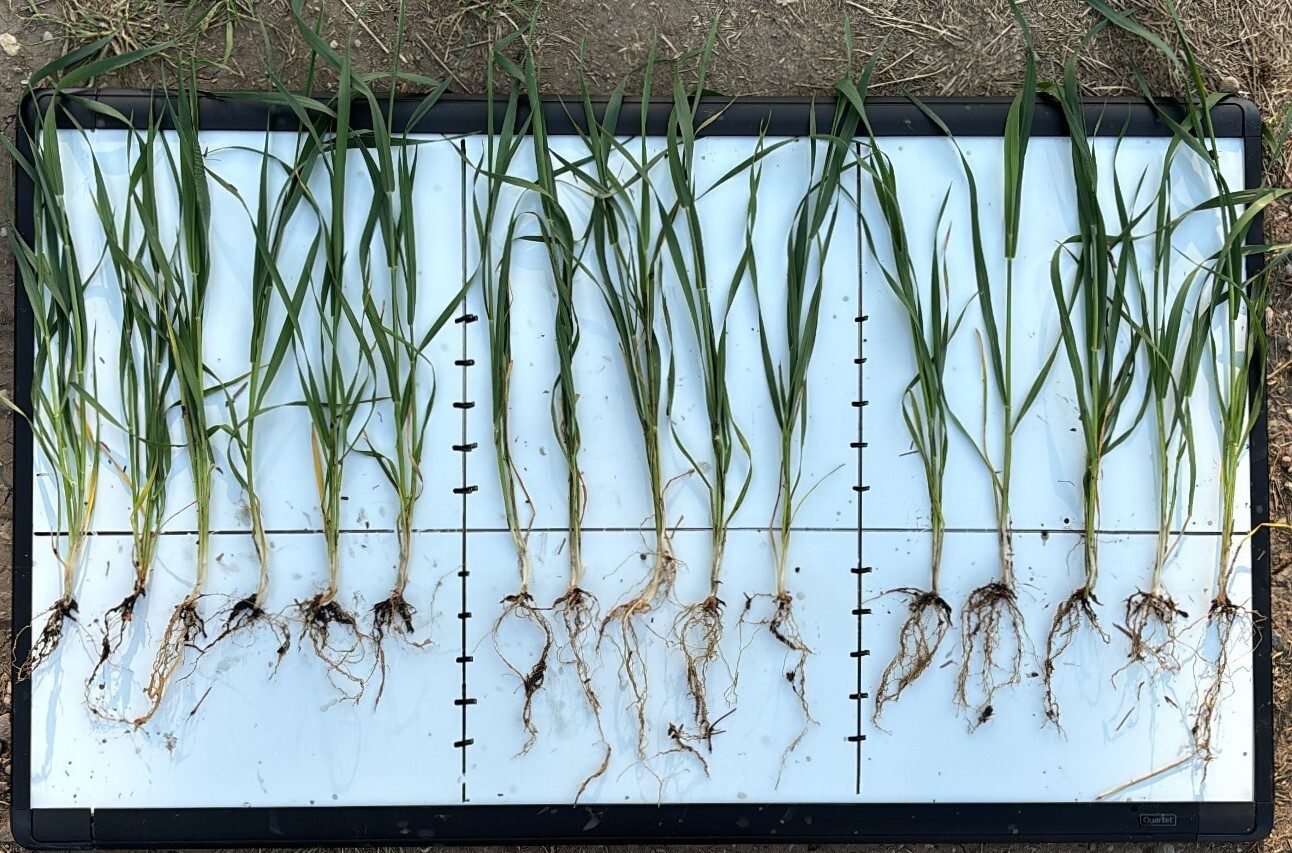
In spring, dig soil samples in areas where you suspect wireworms. Wireworm feeding happens primarily underground. Be aware that in dry conditions, wireworms can burrow up to one meter deep.
Remember, fields with wireworms can be impacted for several years due to the pest's long lifecycle. Practicing a crop rotation strategy can help reduce populations and mitigate the devastation to prime crops.